Chest Pain¶
Claire Lo
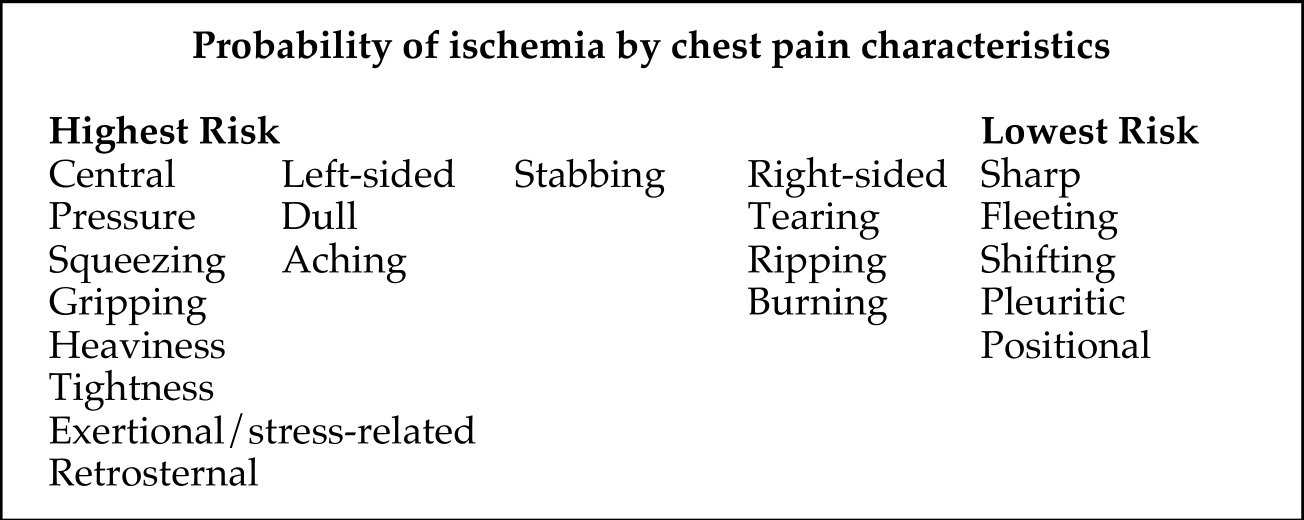
Chest Pain / Angina:¶
- Symptoms determine likelihood that chest pain has a cardiac etiology
- Cardiac > possible cardiac > noncardiac is more useful than typical vs atypical angina
Diagnoses Not to Miss: “The Serious Six” (3 Heart, 2 Lung, 1 Esophagus)¶
- Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Aortic Dissection/Aneurysm
- Cardiac Tamponade
- Pneumothorax
- Pulmonary Embolus
- Mediastinitis (e.g, esophageal perforation)
Other Differential Diagnoses¶
- Skin/subcutaneous: Laceration, herpes zoster, cellulitis, abscess
- Musculoskeletal: Costochondritis, rib fracture, myositis, sprain/strain
- Pleural space (no pain receptors in the lung): PNA, tumor, pleuritis
- Heart: Myocarditis, pericarditis, spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD), coronary vasospasm, aortic stenosis, stress-induced cardiomyopathy (Takotsubo), decompensated heart failure
- GI: GERD, esophagitis, rupture, impaction, diaphragmatic hernia
- Trachea: Tracheitis, tracheal tear
- Nervous system: thoracic radiculopathy
Physical Exam¶
- Vitals: BP in both arms (do while interviewing - quick, easy, inexpensive)
- Hemodynamic profile (warm/dry, warm/wet, cold/dry, cold/wet)
- Palpate chest: evaluate costochondral junction, subcutaneous emphysema, examine skin
- Cardiac: murmurs, rub for pericarditis, JVD for heart failure or PE with RV strain
- Pulm: absent breath sounds for PTX, crackles for left heart failure, PNA
- Abdomen: abdominal pain mistaken or referred as chest pain
- Extremities: asymmetric leg swelling (>2 cm difference) for DVT/PE
Diagnostic Studies¶
- EKG: ACS (STEMI, new LBBB, ST depressions, TWI, Wellens sign), pericarditis, pericardial effusion
- Labs: Troponin (ACS, PE, myocarditis), CBC, BNP, lactate
- CXR: PTX, PNA, dissection, esophageal rupture
- Bedside ultrasound: pericardial effusion, R heart strain for PE, wall motion abnormality for infarct/ischemia or stress-induced CM, valvular disease, lung sliding/PTX
- CTA: gold standard for PE. Dissection can be diagnosed w/ CTA, MRA, or TEE
Evaluation for Coronary Disease |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Indications | Benefits | Risks | Considerations |
| EKG Stress | Low to Intermediate risk patients Do not stress active or suspected ACS Serves as screening with high NPV |
Functional status w/ Bruce treadmill protocol | Exercise tolerance limits use |
Cannot have LBBB, nondiagnostic if 85% target HR not achieved |
| Dobutamine Echo Stress | More sensitive than EKG | Contraindicated: arrhythmias, LVOT obstruction, HTN, AS | Can be useful to eval low grade low flow AS Hold BB |
|
| SPECT stress | More sensitive than echo, Assess viability |
Adenosine or Regadenason contraindicated in reactive airway disease | No caffeine or theophylline prior | |
| PET stress | Better PPV than Echo Assess viability |
Better for pts with larger abdominal girth (less diaphragmatic attenuation) | ||
| Cardiac MRI | Assesses viability | Can assess nonischemic vs ischemic cardiomyopathy; HR must be < 70, gold standard for structure and function | ||
| Coronary CT | Very high NPV for stenosis | Contrast media reactions CIN lower risk than cath |
Might have poor lumen visualization if heavy calcium burden HR < 70 |
|
| Coronary Angiogram | STEMI High risk NSTEMI: Refractory angina, new arrhythmia, cardiogenic shock (HF) Suspected true ACS Diagnostic and Therapeutic |
Direct visualization of lumen Therapeutic PCI |
CIN with contrast Cath site complications Rare: SCAD, cholesterol emboli |
Positive Screen (above) necessitates LHC Case request cath lab NPO MN prior Groin check if femoral access |