Basic Abdominal X-ray Interpretation¶
Often referred to as a KUB or GUAB film.
As with chest radiographs, use a systematic approach. Here are some important reminders:
-
Positioning
- Supine films poorly evaluate for free air, but are fine for evaluating bowel gas pattern and tube positioning
- Upright (preferred) or left lateral decubitus are more sensitive for free air
-
Lines/Tubes
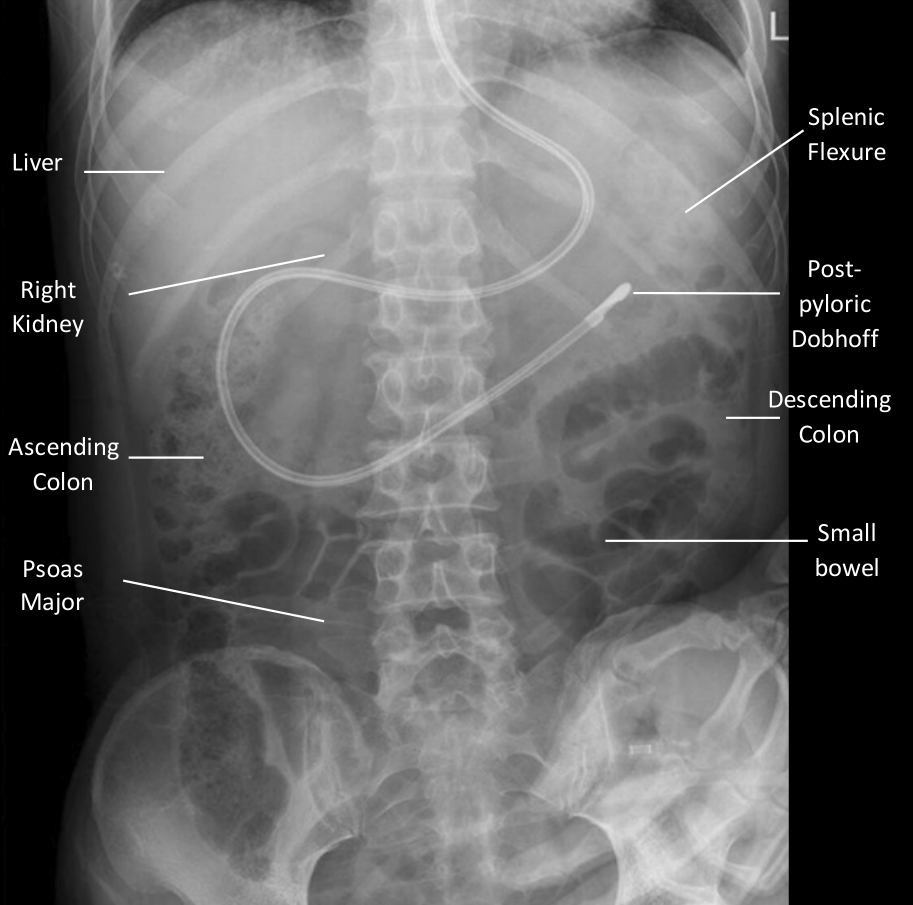
- Enteric tubes come in two general types at VUH – NG/Suction (one radiopaque line) and Dobhoff/Feeding (two radiopaque lines with an opaque tip)
- Enteric tubes should course midline inferior to the carina before taking a smooth rightward curve below the diaphragm and past the GE junction
- Ideally, the tip and terminal sidehole of an NG tube should be below and oriented away from the GEJ
- If post-pyloric placement is desired, the tube should terminate right of midline and resemble the “C-loop” of the duodenum
- NGT radiograph will not include the lower abdomen or upper chest, so cannot fully evaluate bowel gas pattern. If the NGT is in the patient but not seen on the film, confirm that it is not coiled in the oropharynx, esophagus, or airway (confirm with CXR if necessary)
-
Bowel
- Small bowel should be <3 cm, Large <6 cm, Cecum <9 cm; however a normal abdominal plain film cannot rule out obstruction
- Presence of air in the rectum generally favors ileus rather than obstruction
- Some seek to quantify stool burden by abdominal plain film, but this is insensitive and without objective thresholds
-
Pathologic Gas
- Look for lucency adjacent to straight, opaque structures inclyding the diaphragm, liver, and falciform (football sign)
- Subdiaphragmatic
- Outlines the serosal border of bowel (Rigler sign)
- Bowel wall shouldn’t have gas (pneumatosis)
- Liver gas can be pneumobilia (prior ERCP/stent) or portal venous gas (from ischemic bowel)
-
Stones and Bones
- Kidney stones (Low dose CT Kidney Stone protocol is the preferred imaging modality for surveillance)
- Incidental rib fractures, spine compression deformities, pelvic/hip fractures - Ingested foreign bodies
- Surgical clips, embolic coils
-
Masses and Soft Tissue
- The paucity of bowel gas or abnormal contour of intraluminal bowel gas can suggest a soft tissue mass in the abdomen, though this is better evaluated on CT
- Kidney margins may be faintly visible, which is normal
-
Bladder: Foley projecting in right location?
KUB example