Hyperthyroidism¶
Griffin Bullock, Lauren Waskowicz
Background¶
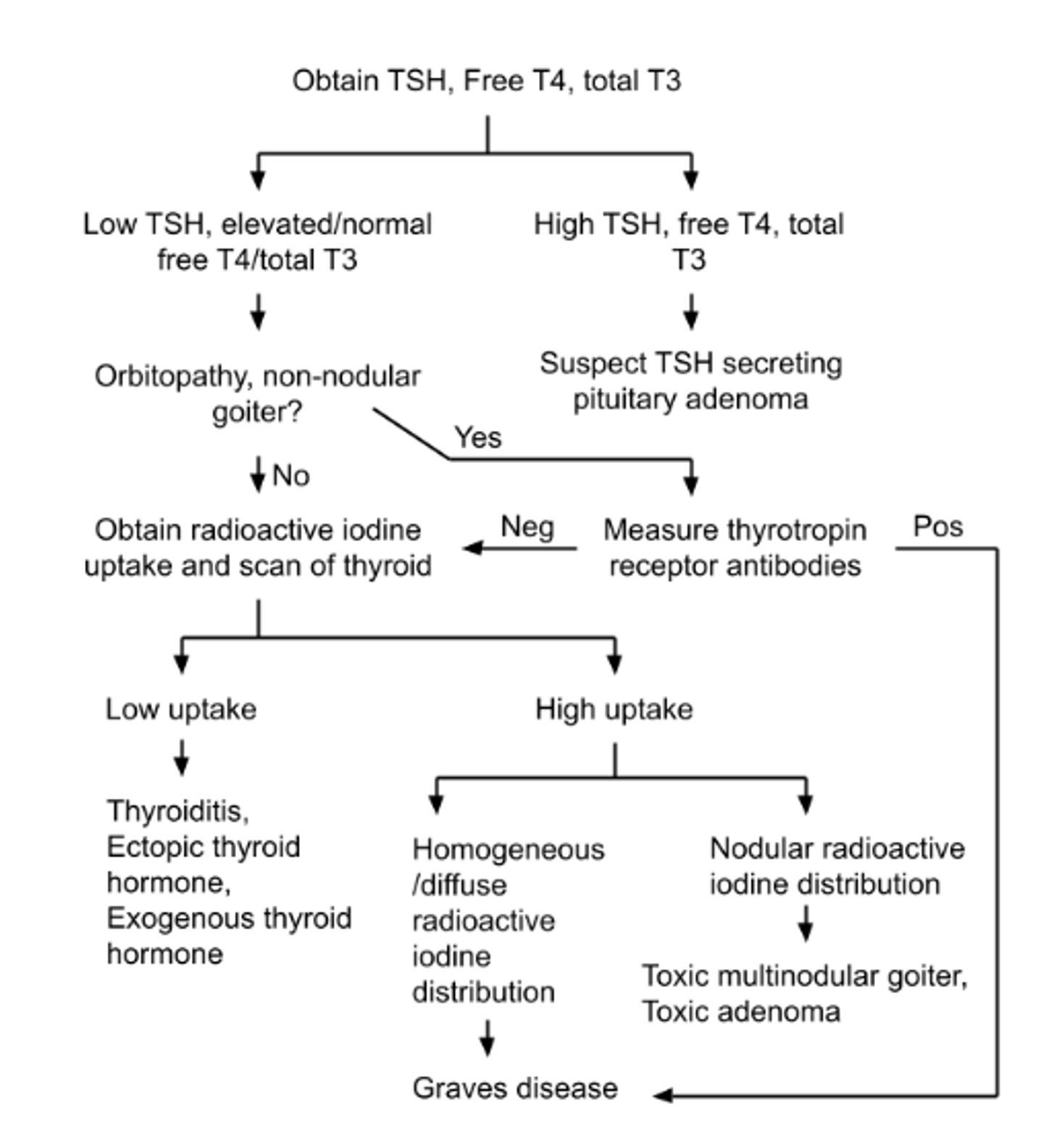
- Excess thyroid hormone caused by increased synthesis, excessive release of preformed thyroid hormone or endogenous/exogenous release of hormone from extrathyroid source
- Low TSH and High T4 and/or T3 (primary): Graves’, Toxic goiter, TSH-producing adenoma, hyperemesis gravidarum, subacute granulomatous thyroiditis, amiodarone, radiation, excessive replacement, struma ovarii
- Low TSH/Normal T4 and T3: Subclinical hyperthyroidism, central hypothyroidism, non-thyroidal illness, recovery from hyperthyroidism, pregnancy (physiologic)
- Subclinical Hyperthyroidism: repeat testing to verify abnormality is not transient
Presentation¶
- Sx: Heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, anxiety, weight loss (w/ normal/increased appetite), increased BM frequency, SOB
- Physical Exam: Goiter, tachycardia/Afib, stare/lid lag, marked muscle weakness (rare presentation of thyrotoxic periodic paralysis), hyperreflexia
- Graves Specific Findings: proptosis/exophthalmos, infiltrative dermopathy (localized or pretibial myxedema)
Evaluation¶
- TSH, free T4, free T3 (only T3 or T4 may be elevated, though both often are)
- Biotin affects assay, causes falsely ↓ TSH and falsely ↑ FT4/FT3
- CBC: may have a normocytic anemia due to increased plasma volume
Management¶
- Methimazole, PTU, beta blockers, radioiodine ablation, surgery
- Endocrine referral