Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)¶
Will Bassett, Matthew Gonzalez
Background¶
- Classically in type 1 diabetes but can also occur in insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes
- Definition: ↑ blood glucose (typically >350) w/ high anion gap and ketones in blood/urine
- If glucose is significantly elevated but little to no ketones/anion gap present, you likely have HHS, which is typically associated with ↑ serum osm and BG > 600
Evaluation¶
- Labs: BMP with anion gap (AG), CBC, phos, blood gas, serum osms, UA, consider beta-hydroxybutyrate
- Workup aimed at discovering the underlying cause (The "I’s"):
- Infection/ Inflammation: CBC, CXR, UA/UCx, LFTs; consider BCx, lipase (pancreatitis). Note: Leukocytosis will be present in DKA, even if infection isn’t the precipitating factor
- Ischemia (MI, CVA, mesenteric ischemia): EKG, Troponin, CT(A) if clinical suspicion
- Intoxication - Ethanol (can cause ketosis with or without acidosis), cocaine, MDMA
- Impregnation - Beta HCG if appropriate
- Insulin-openia/Iatrogenic: steroids, SGLT2 inhibitors, other meds, insulin delivery failure (pump failure, insulin degraded by heat, etc.)
- Remember to correct sodium for hyperglycemia (Na + 2.4mEq * (BG-100))
Management¶
- Initial monitoring: q2-4h BMPs (monitor K closely), q1h BG finger sticks
- Can space less frequently once gap is closed x 2 and pt off insulin infusion
- Ensure IV access
- Start IV fluids, insulin, and potassium as below
- Start insulin gtt
- Start subcutaneous long-acting insulin as soon as insulin drip/IV insulin is started
- Either start home long-acting (dose reduce as needed) or if insulin naïve, Lantus 0.2-0.3u/kg/day
- Lactated ringers’ preferred fluid if no contraindication
- Dextrose should be added when BG <200 (or clear liquid diet)
- Turn off insulin drip when anion gap is closed/bicarb has normalized on two consecutive BMPs
- Consult endocrinology early
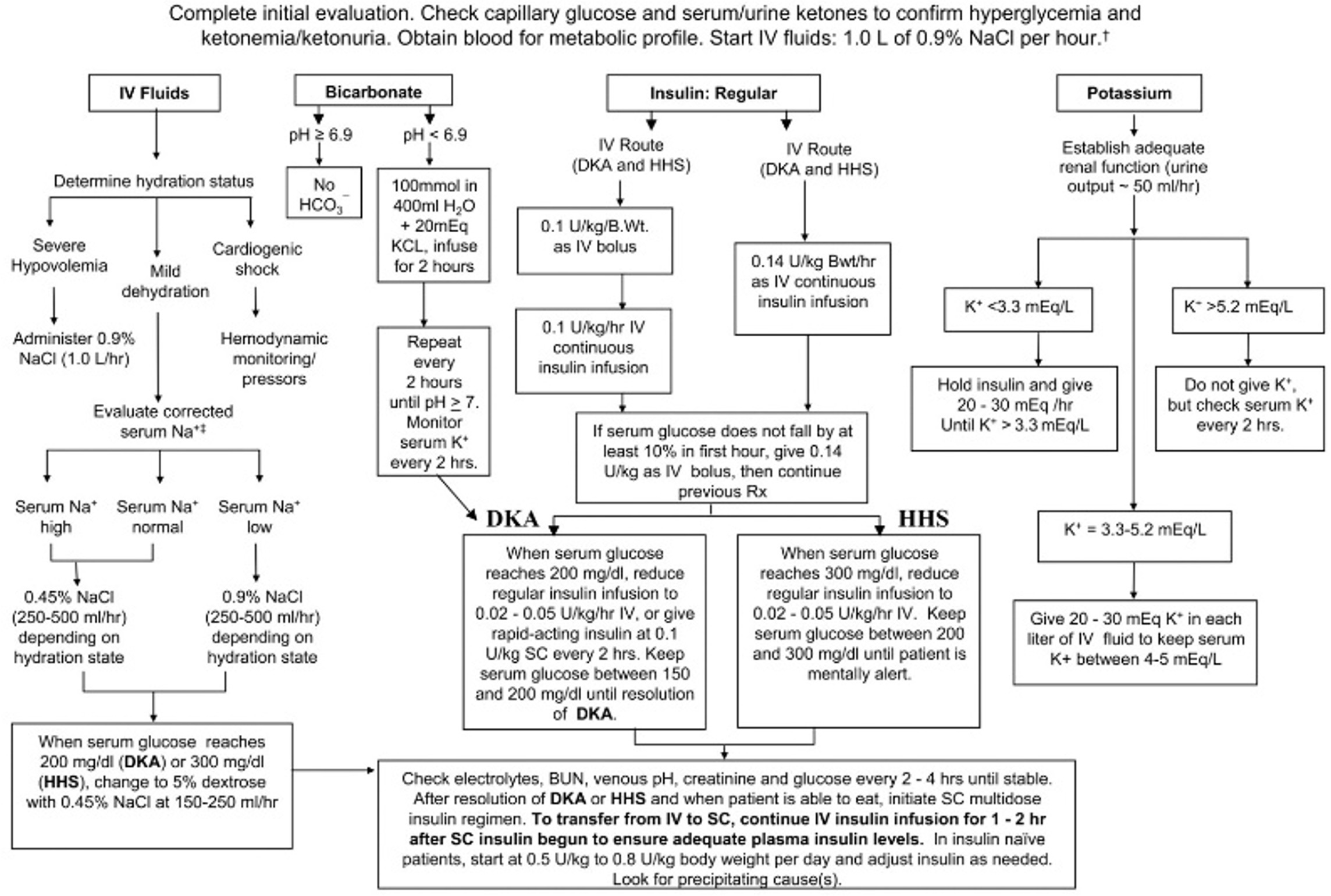
- Management algorithm on next page (Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul; 32(7): 1335–1343)
- Note: pts are usually deficient in total body potassium even if serum potassium is high
Additional Information¶
- Pts on insulin drip can be admitted to stepdown (8MCE) with order set
- Pts can be admitted to stepdown on a subcutaneous insulin protocol with mild DKA with endocrinology guiding insulin management
- Avoid ordering C-peptide if concern for new type 1 diabetes, beta islet cells can be "stunned" with recent hyperglycemic states and may be falsely low
- SGLT2 inhibitors, are being prescribed much more often and can cause a euglycemic DKA, where acidosis and ketosis present but no elevated BG