ABCDEF (A2F) Bundle¶
Kaele Leonard
Background¶
- Post-Intensive Care Syndrome (PICS): complex constellation of cognitive, physical, and psychological impairments that impact most survivors of critical illness, leading to disability, frailty, and poor quality of life
- Predicted by (1) duration of immobility and (2) delirium
- Both are reduced by >80% compliance with ABCDEF (A2F) Bundle concepts
- ABCDEF (A2F) Bundle: Interprofessional, evidence-based safety bundle of care principles to help reduce LOS, mortality, bounce-backs, and the duration of ICU delirium and coma
- Goal: allow pt to “prove us wrong” about readiness for liberation from devices, sedatives, etc.
Assess, prevent, and manage pain¶
- Tools to assess pain using facial expressions, body movements, muscle tension, compliance with ventilator, or vocalization for extubated pts
- Ex: Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT): scale 0-8, uncontrolled pain >=3
- Uncontrolled pain increases risk for delirium, limits inspiratory effort & weaning from ventilator, and limits ability to mobilize
- Treatment: multi-modal: parenteral opioids, neuropathic meds (e.g., gabapentin, ketamine), adjunctive non-opioids analgesics (e.g., acetaminophen, NSAIDs), nonpharmacologic interventions (repositioning, heat/cold)
Both spontaneous awakening trials (SATs) and spontaneous breathing trials (SBTs)¶
- SATs = daily sedative interruptions
- RN-driven protocol involving safety checklist: no active seizures, alcohol withdrawal, agitation, paralytics, myocardial infarction, or increased ICP
- If pass SAT, proceed to SBT
- If fail SAT (anxiety, agitation, pain, resp distress) restart sedation at ½ doses
- SBTs = PS ventilation (Fi02 ≤ 50%, PEEP ≤ 7.5; typically 40% and 5/5) for ≥ 30 minutes
- RT or physician/APP-driven protocol with safety screen: passed SAT, O2 sat ≥ 88%, inspiratory efforts, no myocardial ischemia, no/low vasopressor support
- If pass SBT, physician/APP judgment on extubation
- If fail SBT (RR > 35 or < 8, O2 sat < 88%, resp distress, mental status change) restart full ventilatory support
- Evidence:
- Liberated pts from mechanical ventilation 3 days sooner, decreased ICU and hospital length of stay by 4 days, and 14% absolute reduction in mortality at 1 year
Choice of analgesia and sedation¶
- Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS): sedation & level of arousal assessment tool (Figure 1)
- Target light sedation of RASS -1 to 0 with goal of (1) pt following commands without agitation and (2) limiting immobilization
- Over-sedation: hold sedatives till target, then restart at ½ prior dose
- Analgosedation with focus on treating pain first and then adding sedation meds PRN
- Sedatives: dexmedetomidine (dex) or propofol >>> benzodiazepines (increased delirium risk)

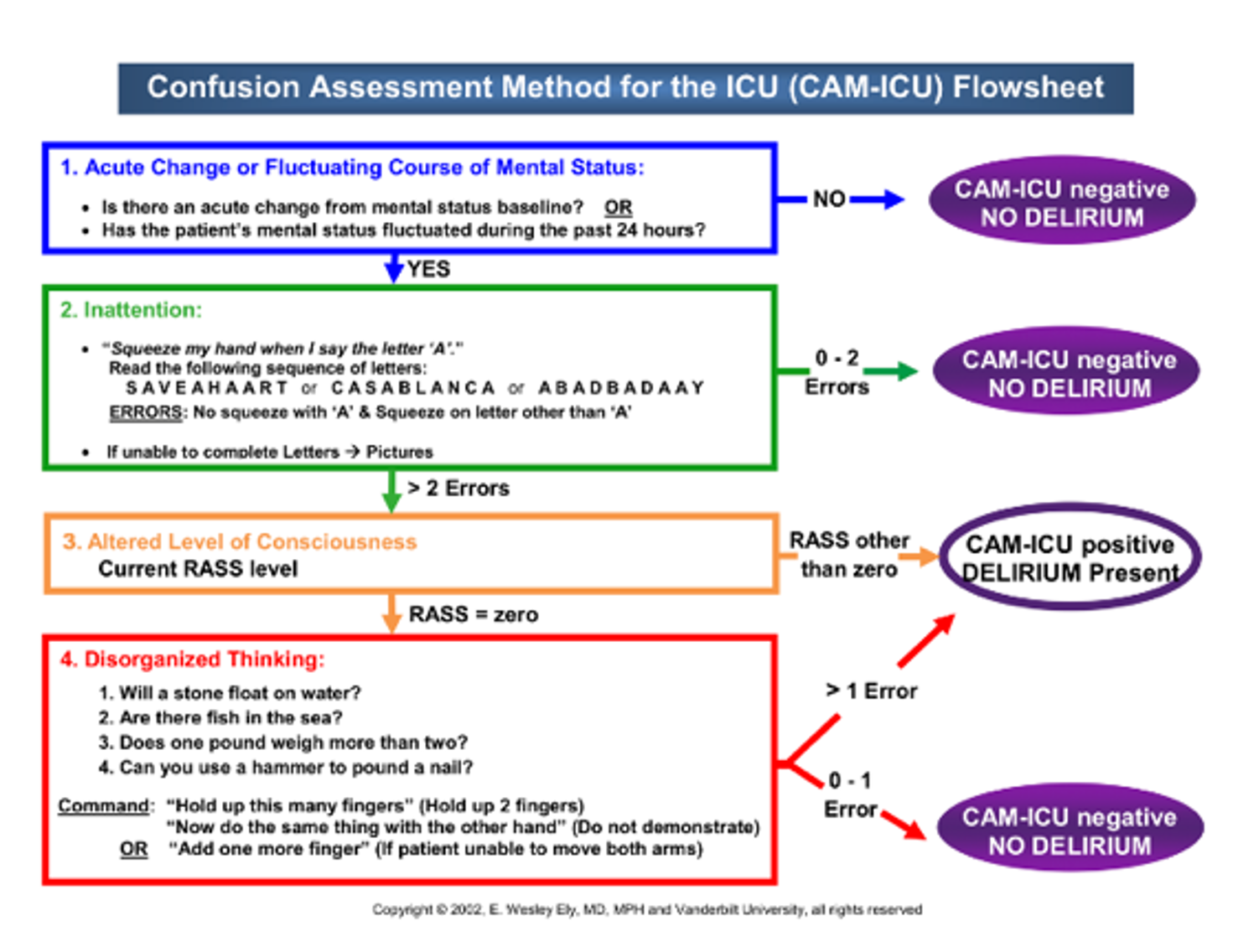
Delirium- assess, prevent, and manage¶
- Screening for delirium: q4h using CAM-ICU (Figure 2)
- Affects 60-80% of ventilated pts and associated with increased morbidity and mortality, longer ICU and hospital length of stay, long-term cognitive dysfunction
- Risk factors and treatment: see Delirium section in Psychiatry
Early mobility and exercise¶
- Prolonged immobilization during critical illness leads to ICU-acquired weakness, associated with worse outcomes: ↑ mechanical ventilation, increased hosp length of stay, greater mortality, and greater disability
- Consult PT/OT to initiate rehab at the beginning of critical illness
- Can be done safely in pts receiving advanced support
Family engagement and empowerment¶
- Especially important when pts are unable to communicate themselves
- Incorporate family at the bedside and on rounds to learn pt preferences and values, engage in shared-decision making, and address questions and concerns